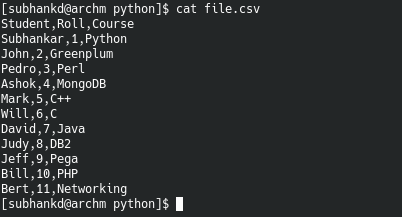
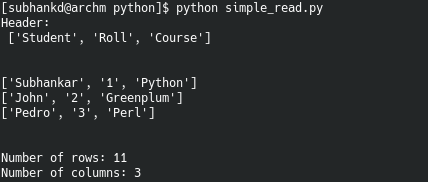
Below is an example code which reads “file.csv”. Assume it contains data from a table with table headers as it’s first row.
We extract the table header with : contents_header = contents[0]
We then remove the table header from dataset by slicing: contents = contents[1:]
Function explore_data() prints rows read from file. It can also show total no. of rows and columns in the data.
from csv import reader
opened_file = open('file.csv')
read_file = reader(opened_file)
contents = list(read_file) #read the contents of file as a list
contents_header = contents[0] #extract only the header
contents = contents[1:] #remove the header
def explore_data(dataset, start, end, rows_and_columns=False):
dataset_slice = dataset[start:end]
for row in dataset_slice:
print(row)
print('\n') # adds a new (empty) line between rows
if rows_and_columns:
print('Number of rows:', len(dataset))
print('Number of columns:', len(dataset[0]))
print('Header : \n', contents_header)
print('\n')
explore_data(contents, 0, 3, True) #print row 0 to 2, Also show no. of rows and columnsExample: